The Lean Startup
344 likes90,536 views
Eric Ries' presentation on lean startups. From Steve Blank's Customer Development course at Berkeley. Learn more and hear the audio at http://bit.ly/3qsvJ.
1 of 27
Downloaded 5,200 times










Recommended
Customer Development at Startup2Startup by Stanford University, has 28 slides with 158668 views.Steve Blank and Eric Ries at Startup2Startup Customer Development Presentation 30 April 2009, Palo Alto California



Customer Development at Startup2StartupStanford University
28 slides•158.7K views
Steve Blank and Eric Ries at Startup2Startup Customer Development Presentation 30 April 2009, Palo Alto CaliforniaLecture 1: Business Model & Customer Development by Stanford University, has 201 slides with 105119 views.The document summarizes the key concepts from the Lean LaunchPad course, including business models, customer development, and pivoting. It explains that a business model describes all parts of a company necessary to make money. It then discusses customer development as a process involving customer discovery, validation, and creation to iteratively build a business model through pivoting based on customer feedback. The goal is to identify a repeatable and scalable business model in the search for a startup idea.



Lecture 1: Business Model & Customer DevelopmentStanford University
201 slides•105.1K views
The document summarizes the key concepts from the Lean LaunchPad course, including business models, customer development, and pivoting. It explains that a business model describes all parts of a company necessary to make money. It then discusses customer development as a process involving customer discovery, validation, and creation to iteratively build a business model through pivoting based on customer feedback. The goal is to identify a repeatable and scalable business model in the search for a startup idea.The startup owners manual sxsw by Stanford University, has 123 slides with 91427 views.The document summarizes Steve Blank's presentation on the startup path and customer development process. It provides an overview of Blank's background and books that influenced his work. It then outlines the four steps of the customer development process - customer discovery, validation, creation, and growth. The presentation concludes by discussing how Blank teaches entrepreneurs to test hypotheses about their business model in his Lean LaunchPad class over 8 weeks.



The startup owners manual sxswStanford University
123 slides•91.4K views
The document summarizes Steve Blank's presentation on the startup path and customer development process. It provides an overview of Blank's background and books that influenced his work. It then outlines the four steps of the customer development process - customer discovery, validation, creation, and growth. The presentation concludes by discussing how Blank teaches entrepreneurs to test hypotheses about their business model in his Lean LaunchPad class over 8 weeks.A Playbook for Achieving Product-Market Fit by Lean Startup Co., has 64 slides with 2797 views.Dan Olsen, The Lean Product Playbook , @danolsen
Room: C260
Everyone working on a new product is trying to achieve the same goal: product-market fit. Although product-market fit is one of the most important Lean Startup concepts, it’s also the least well defined. Dan Olsen shares the top advice from his book The Lean Product Playbook, including the Product-Market Fit Pyramid: an actionable model that breaks product-market fit down into 5 key elements. Dan also explains the Lean Product Process, a 6-step methodology with practical guidance on how to achieve product-market fit, illustrated with a real-world case study.



A Playbook for Achieving Product-Market FitLean Startup Co.
64 slides•2.8K views
Dan Olsen, The Lean Product Playbook , @danolsen
Room: C260
Everyone working on a new product is trying to achieve the same goal: product-market fit. Although product-market fit is one of the most important Lean Startup concepts, it’s also the least well defined. Dan Olsen shares the top advice from his book The Lean Product Playbook, including the Product-Market Fit Pyramid: an actionable model that breaks product-market fit down into 5 key elements. Dan also explains the Lean Product Process, a 6-step methodology with practical guidance on how to achieve product-market fit, illustrated with a real-world case study.Lecture 1 intro bus model cust dev 120411 by Stanford University, has 236 slides with 34015 views. You will be graded as a team
- No free riders
- Communicate outside of class
- Support each other
- Fail fast and learn quick
The goal is to learn, not get an “A”
We want you to succeed more than you want to pass the class
We are here to help, challenge and support you
This class simulates a startup - it will be hard but also very rewarding
Now go out and start learning!



Lecture 1 intro bus model cust dev 120411Stanford University
236 slides•34K views
You will be graded as a team
- No free riders
- Communicate outside of class
- Support each other
- Fail fast and learn quick
The goal is to learn, not get an “A”
We want you to succeed more than you want to pass the class
We are here to help, challenge and support you
This class simulates a startup - it will be hard but also very rewarding
Now go out and start learning!Lean Startups Steve Blank Eric Ries by Stanford University, has 26 slides with 17697 views.Summary of the strategy of building low-burn-rate startups, i.e. capital efficient and generally frugal. By taking advantage of open source, agile software, and iterative development, lean startups can operate with much less waste.



Lean Startups Steve Blank Eric RiesStanford University
26 slides•17.7K views
Summary of the strategy of building low-burn-rate startups, i.e. capital efficient and generally frugal. By taking advantage of open source, agile software, and iterative development, lean startups can operate with much less waste.Introduction to Lean Startup » Lean Startup Barcelona by Jaume Teixi, has 32 slides with 9583 views.Lean Startup BCN
Inaugural Meeting
La Salle ~ Barcelona
29/03/2012
Lean Startup BCN
@LeanStartupBCN



Introduction to Lean Startup » Lean Startup BarcelonaJaume Teixi
32 slides•9.6K views
Lean Startup BCN
Inaugural Meeting
La Salle ~ Barcelona
29/03/2012
Lean Startup BCN
@LeanStartupBCNLean Startup by Manik Choudhary , has 27 slides with 2021 views.This document discusses the Lean Startup methodology. It notes that the vast majority of new products and startups fail. The Lean Startup approach was developed by Eric Ries to help startups search for a scalable and profitable business model through experimentation and customer feedback. It advocates developing a minimum viable product and using the build-measure-learn process to continually pivot based on learning. The Lean Startup principles of validating learning and innovation accounting are also summarized.



Lean StartupManik Choudhary
27 slides•2K views
This document discusses the Lean Startup methodology. It notes that the vast majority of new products and startups fail. The Lean Startup approach was developed by Eric Ries to help startups search for a scalable and profitable business model through experimentation and customer feedback. It advocates developing a minimum viable product and using the build-measure-learn process to continually pivot based on learning. The Lean Startup principles of validating learning and innovation accounting are also summarized.Getting to Product Market Fit - An Overview of Customer Discovery & Validation by Jason Evanish, has 46 slides with 30410 views.An overview of the first two stages of Steve Blank's Four Steps to the Epiphany: Customer Discovery and Customer Validation. Includes in depth advice on the customer development interview as well.
I'm writing a book on How to Build Customer Driven Products based on tactics like the ones in this presentation. You can sign up to learn more here: http://eepurl.com/RZoO9



Getting to Product Market Fit - An Overview of Customer Discovery & ValidationJason Evanish
46 slides•30.4K views
An overview of the first two stages of Steve Blank's Four Steps to the Epiphany: Customer Discovery and Customer Validation. Includes in depth advice on the customer development interview as well.
I'm writing a book on How to Build Customer Driven Products based on tactics like the ones in this presentation. You can sign up to learn more here: http://eepurl.com/RZoO9Why Product Managers Need Sneakers by Stanford University, has 81 slides with 31336 views.- Product managers at startups need to wear sneakers because they must actively search for customers outside the building, unlike at large companies where customers are known.
- Startups go through phases of customer discovery, validation, and creation where hypotheses about customers and products are tested iteratively through contact with potential users.
- There are three types of markets that determine how startups should approach sales, marketing, and business development - existing, resegmented, and new markets.
- Engineering approaches also differ between startups searching for problems/solutions and large companies executing known requirements. Founders must lead the search while product management can help or hinder it.



Why Product Managers Need SneakersStanford University
81 slides•31.3K views
- Product managers at startups need to wear sneakers because they must actively search for customers outside the building, unlike at large companies where customers are known.
- Startups go through phases of customer discovery, validation, and creation where hypotheses about customers and products are tested iteratively through contact with potential users.
- There are three types of markets that determine how startups should approach sales, marketing, and business development - existing, resegmented, and new markets.
- Engineering approaches also differ between startups searching for problems/solutions and large companies executing known requirements. Founders must lead the search while product management can help or hinder it.Introduction to Customer Development at the Lean Startup Intensive at Web 2.0... by Eric Ries, has 50 slides with 43282 views.The document discusses customer development and the search for a business model in startups. It emphasizes testing hypotheses with customers to validate problems and solutions. There are three types of markets - existing, resegmented, and new - that require different sales, marketing and business development approaches. The key ideas are to parallel customer development with product development using measurable checkpoints tied to customer milestones rather than just product shipments. The goal is to prove a repeatable and scalable business model before scaling the company.



Introduction to Customer Development at the Lean Startup Intensive at Web 2.0...Eric Ries
50 slides•43.3K views
The document discusses customer development and the search for a business model in startups. It emphasizes testing hypotheses with customers to validate problems and solutions. There are three types of markets - existing, resegmented, and new - that require different sales, marketing and business development approaches. The key ideas are to parallel customer development with product development using measurable checkpoints tied to customer milestones rather than just product shipments. The goal is to prove a repeatable and scalable business model before scaling the company.Stanford Entrepreneurship Week 030211 by Stanford University, has 107 slides with 20336 views.The document discusses how startups have traditionally operated with high costs and long development times, leading to slow customer adoption, high failure rates, and innovation limited to a few regions. However, it notes an "entrepreneurial explosion" is now occurring, enabled by low startup costs, short development times, fast customer adoption, global innovation, and large pools of risk capital. It distinguishes between small businesses, large company innovation, and scalable startups. Scalable startups search for a business model through customer development and agile development, rather than executing a predetermined plan, in order to transition successfully from startup to large company.



Stanford Entrepreneurship Week 030211Stanford University
107 slides•20.3K views
The document discusses how startups have traditionally operated with high costs and long development times, leading to slow customer adoption, high failure rates, and innovation limited to a few regions. However, it notes an "entrepreneurial explosion" is now occurring, enabled by low startup costs, short development times, fast customer adoption, global innovation, and large pools of risk capital. It distinguishes between small businesses, large company innovation, and scalable startups. Scalable startups search for a business model through customer development and agile development, rather than executing a predetermined plan, in order to transition successfully from startup to large company.Successful entrepreneurship 1 by Stanford University, has 102 slides with 121956 views.The document provides advice for creating a successful startup. It discusses that Mike, an experienced executive, had a great idea for a product but some key mistakes. It outlines 5 lessons: 1) No business plan survives customer contact. 2) Have a clear business model. 3) Consider alternative models. 4) Treat your model as hypotheses to test. 5) Verify your model before building your company to avoid wasting money. It emphasizes the importance of testing assumptions through customer development and pivoting the model until it is proven.



Successful entrepreneurship 1Stanford University The document provides advice for creating a successful startup. It discusses that Mike, an experienced executive, had a great idea for a product but some key mistakes. It outlines 5 lessons: 1) No business plan survives customer contact. 2) Have a clear business model. 3) Consider alternative models. 4) Treat your model as hypotheses to test. 5) Verify your model before building your company to avoid wasting money. It emphasizes the importance of testing assumptions through customer development and pivoting the model until it is proven.
Startup Secrets: Wrap Up & Geoffrey Moore - An Insider’s Guide



Startup Secrets: Wrap Up & Geoffrey Moore - An Insider’s GuideMichael Skok The document discusses an agenda for a startup secrets event that will cover topics like value propositions, company formation, business models, go-to-market strategies, and a session with Geoffrey Moore. The agenda indicates there will be presentations and workshops on these topics to provide insights for attendees on developing unfair competitive advantages for their startups. The document also shares examples from companies like Apperian, Acquia, and Demandware to illustrate lessons learned in startup strategies.
Go-to-market strategy for tech startups



Go-to-market strategy for tech startupsSovita Chander The building blocks you need to create your sales and marketing plan for your technology startup. Presented at FastTrac program, Quebec City, Canada.
Customer Discovery Skills 



Customer Discovery Skills Stanford University The goal is to give entrepreneurs hands-on experience with customer discovery techniques like generating hypotheses about customer needs, designing experiments to test hypotheses, and analyzing customer insights.
Turning Products Into Companies



Turning Products Into CompaniesMichael Skok This document provides an overview of how to design products to achieve product-market fit and turn products into companies. It discusses designing for minimum viable products, minimum viable segments, and minimum repeatable products to iteratively test product-market fit. It also covers making "slippery" products that are simple, have low costs, integrate easily, prove value quickly, and are sticky for customers. The goal is to focus products on specific customer needs to facilitate growth.
Venture Design Workshop: Business Model Canvas



Venture Design Workshop: Business Model CanvasAlex Cowan These slides support the various workshops I do and my online curriculum in two principal places:
1. Business Model Canvas Tutorial
This is a more fully articulated instructional, complete with templates: bit.ly/nicebmc.
2. Startup Sprints
This is a structured self-service for Venture Design/new venture creation: bit.ly/startupsprints.
Lean startup 101



Lean startup 101Jason Evanish Jason Evanish gave a presentation on Lean Startups and how to apply Lean principles to new ventures. He discussed that Lean Startups focus on getting customer feedback as early as possible through interviews and minimum viable products, rapidly iterating based on what is learned. Evanish recommended tools like the Lean Canvas and customer development interviews to help follow the Lean process and identify problems to solve rather than features to build. He closed by urging attendees to start applying Lean Startup techniques immediately and provided further resources on the topic.
Eric Ries - The Lean Startup - Google Tech Talk



Eric Ries - The Lean Startup - Google Tech TalkEric Ries This document discusses Lean Startup principles including validated learning, building-measuring-learning quickly through iterations, and innovation accounting. It emphasizes that entrepreneurship is management, startups are experiments, and most successful startups pivot their vision based on customer feedback. The Lean Startup methodology advocates for developing minimum viable products and continuously deploying, measuring and improving through techniques like A/B testing to rapidly learn what customers want.
Lean Startup



Lean StartupJohn Greene The document discusses different types of startups: Lifestyle startups focus on passion projects with small revenues. Small business startups aim to support a family with a known product. Scalable startups search for a business model to grow big with unknown customers/features. Buyable startups seek an exit through acquisition. The document also discusses sustaining/disruptive innovation at large companies and social entrepreneurship. It defines a startup as searching for a repeatable, scalable business model under uncertainty. The lean startup process is presented as a solution to validate learning through frequent experiments and customer feedback over rigid plans.
Customer Development/Lean Startup 011910 Class 1



Customer Development/Lean Startup 011910 Class 1Stanford University This document provides an introduction to an advanced entrepreneurship course on customer development and the lean startup methodology. It outlines the course objectives, prerequisites, structure, and key concepts that will be covered, including reducing product/market risk, customer development process of discovery, validation, and creation, and building companies with low costs by designing for learning rather than traditional product development processes. The instructors are introduced as Steve Blank and Eric Ries, pioneers of the lean startup approach.
Startup Secrets - Turning Products into Companies



Startup Secrets - Turning Products into CompaniesMichael Skok This document provides an overview of turning products into companies by closing the "product company GAP." It discusses designing products for market fit by focusing on a primary value proposition for a single audience. It introduces the concepts of minimum viable product, minimum viable segment, and minimum repeatable product to test market fit in smaller segments. The document also discusses architecting business models, including designing "slippery" products, and using Russian doll pricing and packaging strategies. The goal is to help startups transition from developing products to building successful companies by considering business model, go-to-market strategy, and how the product will influence these from the beginning.
Value Proposition Design



Value Proposition DesignYves Pigneur The document discusses tools and processes for designing and testing value propositions for businesses. It describes using the Value Proposition Canvas tool to iteratively search for value propositions that customers want through designing, testing, and evolving propositions. It emphasizes managing the non-linear process of value proposition design by systematically applying tools like the Canvas to reduce risk.
Lean startup, customer development, and the business model canvas



Lean startup, customer development, and the business model canvasgistinitiative The document discusses key concepts in lean startup methodology, including building business models focused on customer development rather than business plans, developing minimum viable products to test hypotheses, and using an iterative build-measure-learn process. It provides examples of how startups should focus on building products that solve customer pains and create gains rather than features, and emphasizes conducting customer interviews to gather evidence and test hypotheses about the business model.
Business model innovation



Business model innovationDavid Skok The document discusses business model innovation and key lessons learned from case studies. It emphasizes the importance of balancing the cost to acquire customers (CAC) with the lifetime value (LTV) of customers. Business models that use free trials, freemium options, and viral marketing can achieve low CAC through inbound marketing techniques. Recurring subscription revenue models provide predictability and allow companies to scale through efficient sales processes.
Product Management for Startups by Dan Olsen



Product Management for Startups by Dan OlsenDan Olsen My Product Management talk from the NextGen Conference at Stanford on Nov 14, 2009.
Summary of The Lean Startup (Eric Ries)



Summary of The Lean Startup (Eric Ries)Vinsol This is summary of what Eric Ries has mentioned in his book The Lean Startup. Guides everyone who is looking out to start his own venture.
An Intro to Lean Startup



An Intro to Lean StartupRyan Hoover This is an internal “brown bag” presentation I did at PlayHaven, introducing the fundamentals of Lean Startup methodology. Unfortunately, the Cookie Monster GIF doesn’t animate in the Slideshare presentation but you enjoy it 24/7 by clicking this link: http://gifsoup.com/view/1836944/cookie-monster.html :)
Also note that you may notice a few jumps in the included audio recording - I had to remove some sensitive material.
Ryan
@rrhoover
http://ryanhoover.me
The Lean Startup - Visual Summary



The Lean Startup - Visual SummaryBrett Suddreth The document summarizes key principles from Eric Ries' book on building successful startups using a "Lean" approach. It discusses 5 principles: (1) entrepreneurs are everywhere, (2) entrepreneurship is management, (3) startups exist to learn how to build a sustainable business through validated learning, (4) the build-measure-learn cycle allows for rapid iteration, and (5) innovation accounting helps prioritize work. It emphasizes the importance of rapid prototyping to validate assumptions and learn quickly from customers through metrics. Pivoting the business model based on learnings, rather than stubbornly sticking to initial ideas, is also highlighted as critical to the Lean approach for building enduring businesses.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Getting to Product Market Fit - An Overview of Customer Discovery & Validation



Getting to Product Market Fit - An Overview of Customer Discovery & ValidationJason Evanish An overview of the first two stages of Steve Blank's Four Steps to the Epiphany: Customer Discovery and Customer Validation. Includes in depth advice on the customer development interview as well.
I'm writing a book on How to Build Customer Driven Products based on tactics like the ones in this presentation. You can sign up to learn more here: http://eepurl.com/RZoO9
Why Product Managers Need Sneakers



Why Product Managers Need SneakersStanford University - Product managers at startups need to wear sneakers because they must actively search for customers outside the building, unlike at large companies where customers are known.
- Startups go through phases of customer discovery, validation, and creation where hypotheses about customers and products are tested iteratively through contact with potential users.
- There are three types of markets that determine how startups should approach sales, marketing, and business development - existing, resegmented, and new markets.
- Engineering approaches also differ between startups searching for problems/solutions and large companies executing known requirements. Founders must lead the search while product management can help or hinder it.
Introduction to Customer Development at the Lean Startup Intensive at Web 2.0...



Introduction to Customer Development at the Lean Startup Intensive at Web 2.0...Eric Ries The document discusses customer development and the search for a business model in startups. It emphasizes testing hypotheses with customers to validate problems and solutions. There are three types of markets - existing, resegmented, and new - that require different sales, marketing and business development approaches. The key ideas are to parallel customer development with product development using measurable checkpoints tied to customer milestones rather than just product shipments. The goal is to prove a repeatable and scalable business model before scaling the company.
Stanford Entrepreneurship Week 030211



Stanford Entrepreneurship Week 030211Stanford University The document discusses how startups have traditionally operated with high costs and long development times, leading to slow customer adoption, high failure rates, and innovation limited to a few regions. However, it notes an "entrepreneurial explosion" is now occurring, enabled by low startup costs, short development times, fast customer adoption, global innovation, and large pools of risk capital. It distinguishes between small businesses, large company innovation, and scalable startups. Scalable startups search for a business model through customer development and agile development, rather than executing a predetermined plan, in order to transition successfully from startup to large company.
Successful entrepreneurship 1



Successful entrepreneurship 1Stanford University The document provides advice for creating a successful startup. It discusses that Mike, an experienced executive, had a great idea for a product but some key mistakes. It outlines 5 lessons: 1) No business plan survives customer contact. 2) Have a clear business model. 3) Consider alternative models. 4) Treat your model as hypotheses to test. 5) Verify your model before building your company to avoid wasting money. It emphasizes the importance of testing assumptions through customer development and pivoting the model until it is proven.
Startup Secrets: Wrap Up & Geoffrey Moore - An Insider’s Guide



Startup Secrets: Wrap Up & Geoffrey Moore - An Insider’s GuideMichael Skok The document discusses an agenda for a startup secrets event that will cover topics like value propositions, company formation, business models, go-to-market strategies, and a session with Geoffrey Moore. The agenda indicates there will be presentations and workshops on these topics to provide insights for attendees on developing unfair competitive advantages for their startups. The document also shares examples from companies like Apperian, Acquia, and Demandware to illustrate lessons learned in startup strategies.
Go-to-market strategy for tech startups



Go-to-market strategy for tech startupsSovita Chander The building blocks you need to create your sales and marketing plan for your technology startup. Presented at FastTrac program, Quebec City, Canada.
Customer Discovery Skills 



Customer Discovery Skills Stanford University The goal is to give entrepreneurs hands-on experience with customer discovery techniques like generating hypotheses about customer needs, designing experiments to test hypotheses, and analyzing customer insights.
Turning Products Into Companies



Turning Products Into CompaniesMichael Skok This document provides an overview of how to design products to achieve product-market fit and turn products into companies. It discusses designing for minimum viable products, minimum viable segments, and minimum repeatable products to iteratively test product-market fit. It also covers making "slippery" products that are simple, have low costs, integrate easily, prove value quickly, and are sticky for customers. The goal is to focus products on specific customer needs to facilitate growth.
Venture Design Workshop: Business Model Canvas



Venture Design Workshop: Business Model CanvasAlex Cowan These slides support the various workshops I do and my online curriculum in two principal places:
1. Business Model Canvas Tutorial
This is a more fully articulated instructional, complete with templates: bit.ly/nicebmc.
2. Startup Sprints
This is a structured self-service for Venture Design/new venture creation: bit.ly/startupsprints.
Lean startup 101



Lean startup 101Jason Evanish Jason Evanish gave a presentation on Lean Startups and how to apply Lean principles to new ventures. He discussed that Lean Startups focus on getting customer feedback as early as possible through interviews and minimum viable products, rapidly iterating based on what is learned. Evanish recommended tools like the Lean Canvas and customer development interviews to help follow the Lean process and identify problems to solve rather than features to build. He closed by urging attendees to start applying Lean Startup techniques immediately and provided further resources on the topic.
Eric Ries - The Lean Startup - Google Tech Talk



Eric Ries - The Lean Startup - Google Tech TalkEric Ries This document discusses Lean Startup principles including validated learning, building-measuring-learning quickly through iterations, and innovation accounting. It emphasizes that entrepreneurship is management, startups are experiments, and most successful startups pivot their vision based on customer feedback. The Lean Startup methodology advocates for developing minimum viable products and continuously deploying, measuring and improving through techniques like A/B testing to rapidly learn what customers want.
Lean Startup



Lean StartupJohn Greene The document discusses different types of startups: Lifestyle startups focus on passion projects with small revenues. Small business startups aim to support a family with a known product. Scalable startups search for a business model to grow big with unknown customers/features. Buyable startups seek an exit through acquisition. The document also discusses sustaining/disruptive innovation at large companies and social entrepreneurship. It defines a startup as searching for a repeatable, scalable business model under uncertainty. The lean startup process is presented as a solution to validate learning through frequent experiments and customer feedback over rigid plans.
Customer Development/Lean Startup 011910 Class 1



Customer Development/Lean Startup 011910 Class 1Stanford University This document provides an introduction to an advanced entrepreneurship course on customer development and the lean startup methodology. It outlines the course objectives, prerequisites, structure, and key concepts that will be covered, including reducing product/market risk, customer development process of discovery, validation, and creation, and building companies with low costs by designing for learning rather than traditional product development processes. The instructors are introduced as Steve Blank and Eric Ries, pioneers of the lean startup approach.
Startup Secrets - Turning Products into Companies



Startup Secrets - Turning Products into CompaniesMichael Skok This document provides an overview of turning products into companies by closing the "product company GAP." It discusses designing products for market fit by focusing on a primary value proposition for a single audience. It introduces the concepts of minimum viable product, minimum viable segment, and minimum repeatable product to test market fit in smaller segments. The document also discusses architecting business models, including designing "slippery" products, and using Russian doll pricing and packaging strategies. The goal is to help startups transition from developing products to building successful companies by considering business model, go-to-market strategy, and how the product will influence these from the beginning.
Value Proposition Design



Value Proposition DesignYves Pigneur The document discusses tools and processes for designing and testing value propositions for businesses. It describes using the Value Proposition Canvas tool to iteratively search for value propositions that customers want through designing, testing, and evolving propositions. It emphasizes managing the non-linear process of value proposition design by systematically applying tools like the Canvas to reduce risk.
Lean startup, customer development, and the business model canvas



Lean startup, customer development, and the business model canvasgistinitiative The document discusses key concepts in lean startup methodology, including building business models focused on customer development rather than business plans, developing minimum viable products to test hypotheses, and using an iterative build-measure-learn process. It provides examples of how startups should focus on building products that solve customer pains and create gains rather than features, and emphasizes conducting customer interviews to gather evidence and test hypotheses about the business model.
Business model innovation



Business model innovationDavid Skok The document discusses business model innovation and key lessons learned from case studies. It emphasizes the importance of balancing the cost to acquire customers (CAC) with the lifetime value (LTV) of customers. Business models that use free trials, freemium options, and viral marketing can achieve low CAC through inbound marketing techniques. Recurring subscription revenue models provide predictability and allow companies to scale through efficient sales processes.
Product Management for Startups by Dan Olsen



Product Management for Startups by Dan OlsenDan Olsen My Product Management talk from the NextGen Conference at Stanford on Nov 14, 2009.
Summary of The Lean Startup (Eric Ries)



Summary of The Lean Startup (Eric Ries)Vinsol This is summary of what Eric Ries has mentioned in his book The Lean Startup. Guides everyone who is looking out to start his own venture.
Viewers also liked (20)
An Intro to Lean Startup



An Intro to Lean StartupRyan Hoover This is an internal “brown bag” presentation I did at PlayHaven, introducing the fundamentals of Lean Startup methodology. Unfortunately, the Cookie Monster GIF doesn’t animate in the Slideshare presentation but you enjoy it 24/7 by clicking this link: http://gifsoup.com/view/1836944/cookie-monster.html :)
Also note that you may notice a few jumps in the included audio recording - I had to remove some sensitive material.
Ryan
@rrhoover
http://ryanhoover.me
The Lean Startup - Visual Summary



The Lean Startup - Visual SummaryBrett Suddreth The document summarizes key principles from Eric Ries' book on building successful startups using a "Lean" approach. It discusses 5 principles: (1) entrepreneurs are everywhere, (2) entrepreneurship is management, (3) startups exist to learn how to build a sustainable business through validated learning, (4) the build-measure-learn cycle allows for rapid iteration, and (5) innovation accounting helps prioritize work. It emphasizes the importance of rapid prototyping to validate assumptions and learn quickly from customers through metrics. Pivoting the business model based on learnings, rather than stubbornly sticking to initial ideas, is also highlighted as critical to the Lean approach for building enduring businesses.
Lean Startup Key Concepts Overview



Lean Startup Key Concepts OverviewYuki Sekiguchi The document provides an overview of the Lean Startup methodology. It discusses that the goal of a startup is to quickly figure out what customers want and will pay for through systematic experiments. The Lean Startup process involves having a clear vision and testing hypotheses about customer value and growth through a build-measure-learn feedback loop using minimum viable products. It emphasizes validated learning to determine whether to pivot the strategy or persevere based on empirical results.
Steve Jobs' LEAN STARTUP PROJECT MANAGEMENT: How Steve Jobs Planned, Organize...



Steve Jobs' LEAN STARTUP PROJECT MANAGEMENT: How Steve Jobs Planned, Organize...Rod King, Ph.D. Steve Jobs' approach to creating extraordinarily successful products is shrouded in mystery. This presentation introduces a new framework, "Lean Startup Project Management", which can be used to explain Steve Jobs' innovation methodology which was largely intuitive. As the name implies, Lean Startup Project Management focuses on translating into reality ideas and principles from Eric Ries's bestselling book, "The Lean Startup." The core tool of Lean Startup Project Management is the One-Page Lean Startup which is a multilevel dashboard. Whereas existing approaches focus on using a tactical dashboard for Lean Startup Project Management, the One-Page Lean Startup uses 3 integrated dashboards: visionary, strategic, and tactical One-Page Lean Startup. Users end up saving time, money, energy, and lots of other resources. Experiment with the One-Page Lean Startup and provide us with your feedback.
10 Slide Lean Startup MVP Deck Example



10 Slide Lean Startup MVP Deck ExampleBogdan Cirlig This document provides an outline for a startup pitch deck. It includes sections for describing the problem being addressed, the proposed solution, business model, core technology, marketing strategy, competition, team, financial projections, and current status. The presenter is encouraged to customize each section with details about their specific company and solution. Examples are provided for a company creating a hotel booking website and one enabling individuals and small businesses to accept credit card payments without a merchant account.
Four Phases of Customer Development



Four Phases of Customer DevelopmentWilson Kanaday This document outlines a road map for customer discovery, validation, creation, and company building. It provides guidance on formulating hypotheses about customers, problems, competitors and markets. It then guides the user to test hypotheses by gathering customer insights and feedback. Based on learnings, the user iterates or exits. Next, it focuses on validating the business model by preparing sales materials, hiring salespeople, and selling to early adopters. It then covers customer creation through demand generation and positioning. Finally, it addresses scaling the company through mainstream customers, managing growth, and developing functional departments and culture.
Presentation examples for class 2 mkt size and hypotheses testing



Presentation examples for class 2 mkt size and hypotheses testingStanford University The Lean LaunchPad presentation provides examples of hypotheses testing for determining market size and opportunity. It discusses conducting interviews with potential customers, partners, and analysts to size the total available market, served available market, and target market in terms of number of customers and potential revenue. Market examples are also presented for various industries to illustrate calculating market size based on total population and incidence rates.
Introduccion a lean startup



Introduccion a lean startupscalabBle Este documento ofrece una introducción al enfoque Lean Startup para el desarrollo de nuevas empresas. Explica que Lean Startup se centra en la iteración rápida y el aprendizaje validado para descubrir un modelo de negocio viable. Detalla las fases del desarrollo del cliente y cómo usar un MVP para validar hipótesis con clientes potenciales de manera barata. También cubre conceptos como pivotar y los mitos comunes sobre Lean Startup.
Customer Development Past Present Future Steve Blank 111909



Customer Development Past Present Future Steve Blank 111909Stanford University - Steve Blank Presentation
- Nov 09 San Francisco Lean Startup Circle
- Customer Development Past Present Future
Lean Startup 101



Lean Startup 101Lean Startup Co. Phil Dillard, Black Ant, @PhilD0210
The objective of the Lean Startup 101 training is to introduce the concepts, terminology and approaches — and, to help organizations overcome resistance accepting the new approach so that exploration and learning can begin. This practical, interactive session will provide a solid foundation for advanced sessions, including the Lean Startup 201 & 301. This training is designed for practitioners in both the enterprise and in startups who are relatively new to the Lean Startup approach or who are seeking a quick refresher. Lean Startup 101 is a perfect way to kick off your week of Lean Startup!
Thanks to Lean Startup Co.’s law firm, Orrick, for being the sponsor for this track.
Strategic Management: Organizational Design



Strategic Management: Organizational DesignTriune Global There are a number of factors that differentiate small-business operations from large-business operations, one of which is the implementation of a formal organizational structure. Organizational structure is important for any growing company to provide guidance and clarity on specific human resources issues, such as managerial authority. Small-business owners should begin thinking about a formal structure early in the growth stage of their business.
Different types of startups, markets and whys



Different types of startups, markets and whysBlaz Kos This presentation is about various types of startup companies, markets and core competencies.
In the presentation you will learn why market trends are important, why markets always win, how to calculate market size and why you have to start with the strong why.
You will also learn the fundamental difference between established companies and startups. Startups are designed to search and established companies to execute.
How to Size a Market Opportunity — Fast



How to Size a Market Opportunity — FastOpenView Reliable market sizing doesn't have to be as complicated or painstakingly slow as you think. This presentation offers a quick overview of the art and science of market sizing, and offers a step-by-step guide on how to conduct seven fast market sizing approaches.
Final le web london (june 2013)



Final le web london (june 2013)Mark Suster The document discusses the rise of the sharing economy. It argues that economic challenges like unemployment, debt, and scarce resources are driving the growth of collaborative consumption models enabled by new networking technologies. These models allow underutilized assets and skills to be monetized, creating new opportunities for both individuals and businesses. The sharing economy empowers people in developing economies and removes physical boundaries to access global markets. While concerns exist around regulation and data privacy, the networking effects of these new platforms are opening up new peer-to-peer models that are disrupting traditional industries and hierarchies.
Destination marketing



Destination marketingKaren Houston Destination marketing plays a key role in tourism by promoting the image and branding of a destination to attract visitors. The core product being marketed is the destination itself, including its attractions, amenities, accessibility, and perceived image. National tourism organizations in most countries are responsible for destination marketing through promotional campaigns and product development. Their goals are to raise awareness of the country as a visitor destination and maximize long-term tourism benefits. In New Zealand, Tourism New Zealand undertakes destination marketing with the mission of marketing the country as a visitor destination.
Disruptive Innovation And The Bankruptcy Of Polaroid



Disruptive Innovation And The Bankruptcy Of PolaroidChris Sandström Polaroid declared bankruptcy in 2001 due to the disruptive shift from analog to digital photography. While Polaroid invested in digital technology starting in the 1980s, developing sensors with megapixels, it failed to develop a new business model for digital imaging and continued relying on selling film. As digital cameras provided instant photography more cheaply, Polaroid's competitive advantage was destroyed within years. Management became more focused on short-term profits and marketing of existing products rather than developing the new business model needed for digital photography.
Startup Marketing Strategy - Case Study



Startup Marketing Strategy - Case StudyRyan Ruud Startup marketing requires wearing a lot of hats. This startup marketing strategy case study explores building and launching a corporate brand from the ground up for a digital media startup serving financial services.
TEDxESADE talk Service Design for the Sharing Economy



TEDxESADE talk Service Design for the Sharing EconomyClaro Partners Inc. With increased connectivity, networks at both a global and local level are growing rapidly whilst new communities can develop and flourish through digital channels. These allow for resources to be shared, swapped, borrowed and traded; bearing a new economy that favours access over ownership.
This is a dramatically different user experience context that demands a transformation of our approach to service design. In this session we will share findings from our global research that explored the experiences and opportunities involved in moving from an ownership economy to one built on access and sharing. In this presentation we present guidelines for creating value exchange networks and share some tools we’ve developed for creating networked services and business models in the sharing economy.
See also video of the presentation being delivered: http://youtu.be/b22vSxLXMsY
Samsung Sharing: Sharing Economy for Samsung Group



Samsung Sharing: Sharing Economy for Samsung Groupwehome.me, a home sharing on blockchain owned by hosts and guests What does the sharing ecnonomy mean to Samsung Group?
How should Samsung take it as the opportunties?
Startup Team Management



Startup Team ManagementMarcin Pokojski The document discusses best practices for startup team management and development based on the teachings of Steve Blank. It addresses that a startup team should be minimal, including only roles necessary to validate a repeatable and scalable business model. The CEO is responsible for all other functions until a business model is proven. An ideal tech startup team includes a designer, engineer, and developer, with the CEO handling additional responsibilities. The document also outlines the four stages of team development and provides tools and methods for customer development, validation, and pivoting as needed based on customer feedback.
Samsung Sharing: Sharing Economy for Samsung Group



Samsung Sharing: Sharing Economy for Samsung Groupwehome.me, a home sharing on blockchain owned by hosts and guests
Similar to The Lean Startup (20)
Lean Startup presentation for Maples Investments by Steve Blank and Eric Ries



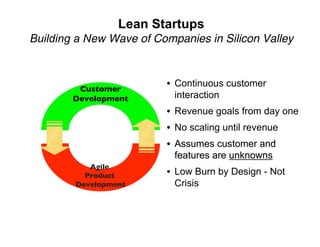
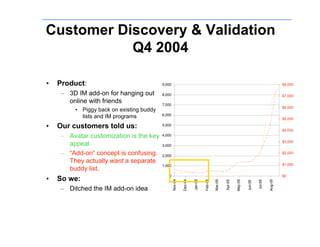
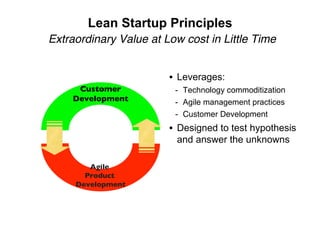
Lean Startup presentation for Maples Investments by Steve Blank and Eric RiesEric Ries The document discusses the lean startup approach which focuses on continuous customer interaction, revenue goals from day one, low burn rates by design rather than crisis, and assuming that customer needs and desired features are unknowns. It provides the example of IMVU, a company that applied lean startup principles by shipping quickly, charging from day one without press releases, and iterating continuously based on customer feedback to achieve $10 million in revenue by 2007 while maintaining a low burn rate.
If you fail to plan, will your plan fail?



If you fail to plan, will your plan fail?MaRS Discovery District Speaker: Kerri Golden, CA and VC
Part of the CIBC Presents Entrepreneurship 101 lecture series.
More information including video: http://www.marsdd.com/Events/Event-Calendar/Ent101/2009/budgeting-02042009.html
Razorfish - Tim Barnes on Consumer Insight



Razorfish - Tim Barnes on Consumer InsightRazorfish Big Idea 3: Consumer Insight was delivered by Razorfish's Tim Barnes on April 22, 2009, at the 9th Annual Razorfish Client Summit (#rzcs on Twitter).
Why CDW



Why CDWKimhig CDW was founded in 1984 and went public in 1993 before being acquired privately in 2007. It generates $8.1 billion in annual sales and services over 450,000 active customers. CDW provides a full range of IT products and services through their account managers, field representatives, and over 800 technical experts. Their large distribution centers allow them to maintain a broad physical inventory and fulfill orders with high accuracy and efficiency.
Comp Plan Dvd[1]![Comp Plan Dvd[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/compplandvd1-123742572231-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Comp Plan Dvd[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/compplandvd1-123742572231-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Comp Plan Dvd[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/compplandvd1-123742572231-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Comp Plan Dvd[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/compplandvd1-123742572231-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Comp Plan Dvd[1]skyallianz The compensation plan document summarizes the compensation structure for SkyAllianz, a multi-level marketing company. There are 4 leadership positions that can be obtained - District Manager, Regional Manager, National Manager, and Vice President. Partners earn money through customer acquisition bonuses, bounty commissions from sales, residual commissions, and position bonuses. The plan emphasizes building a team by sponsoring new partners each month to leverage growth over time through duplication.
08 Q4 Hp Why Cdw



08 Q4 Hp Why CdwJanieroCampbell CDW is a large technology solutions provider founded in 1984 that generates $8.1 billion in annual sales. It has over 450,000 active customers and 2,500 account managers. CDW provides comprehensive technology solutions through its large inventory, technical expertise across various technologies, and strong partnerships with leading vendors such as HP.
Lightyear Wireless Pays You For Your Cellphone Bills



Lightyear Wireless Pays You For Your Cellphone Billskcmgvbs http://www.LightyearWirelessPaysU.com Lightyear Wireless has partnered with 'The Largest And Most Reliable Network" in the US. Get paid residual commissions on wireless phones and wireless internet.
Lightyear Wireless Opportunity Overview



Lightyear Wireless Opportunity Overviewaspengold Lightyear Wireless Business Opportunity enables you to create a Massive Residual Income from Wireless Products and Services 255 Million People Use Everyday.
Nvc kickoff nogiveaway



Nvc kickoff nogiveawaybyunvc This document summarizes the key dates and information for the Miller New Venture Challenge (NVC) competition. It outlines the stages of the competition, including the Big Idea Competition in October, Business Model Competition in January, and NVC Final in April. It provides details on prize amounts that have increased to $135,000 total in 2013. Participants are encouraged to apply by the February 23rd deadline and attend an informational workshop on February 6th. Mentoring and judging opportunities are also described.
MVT Presentation Philippines v1.3



MVT Presentation Philippines v1.3Bong Bong This document outlines ground rules for a business presentation by MVT Eagles, stating that the material is their intellectual property and is meant to develop business partners globally in line with their ethics and guidelines. Presenters must use the material as intended and the company reserves the right to update the presentation over time based on business needs.
mba570.marapr09.class4



mba570.marapr09.class4Lawrence This document outlines the agenda and topics for an MBA course on sustainable customer relationships taking place in December/January 2009. The topics include reviewing major concepts, customer segmentation, perceptual mapping, forecasting, a case study on Classic Airlines, benchmarking customer relationships, and utilizing customer feedback. Students will analyze Classic Airlines and propose initiatives to improve customer acquisition and retention.
Retso worksheets dollinger presentation



Retso worksheets dollinger presentationMatt Dollinger These are the worksheets discussed in my RETSO presentation from Atlanta 2011. These are free to use with your agents (or yourself) please share any thoughts, successes or changes you have made with me.
Using The Numbers To Communicate, Analyze And Run Ppt



Using The Numbers To Communicate, Analyze And Run PptSteve_Rosvold The document provides an overview of key financial statements and metrics that business owners can use to understand, communicate about, and improve their business, including the cash flow statement, balance sheet, and income statement. It discusses how these tools can be used to analyze trends in cash flow, financial position, and profitability over time. Examples and case studies are provided to illustrate how different stakeholders might interpret and apply the information in the statements.
MakeYourMark - UK Gatton MKT600 Presentation (10.11.2011) 



MakeYourMark - UK Gatton MKT600 Presentation (10.11.2011) MakeYourMark The document describes a greeting card and mailing service called Make Your Mark that offers the following:
- Greeting cards for various occasions and automated mailing services for businesses.
- The ability to upload customer contacts, select and personalize cards, schedule deliveries, and automate mailing and fulfillment.
- Their target customer demographics include various professional service businesses like realtors, doctors, and attorneys.
- The document then outlines the services and features in more detail and provides industry statistics on the greeting card market.
Building A Virtual Economy



Building A Virtual EconomyMatt McAllister This document provides an agenda and overview for a MySpace devJam event. The agenda includes a workshop on building a virtual economy, a panel discussion on virtual currency monetization, an app review session, and updates on the MySpace platform. Offerpal is introduced as a social advertising platform that has powered virtual economies for 800+ publishers. Steps are outlined for publishers to build their own virtual economies, including defining currency and ways for users to earn and spend it. Optimization of the virtual economy and use of Offerpal's platform to maximize monetization are also discussed.
Vmobilepowerpointpresentation earn30kincomepermonthusingyourcellphone-1106022...



Vmobilepowerpointpresentation earn30kincomepermonthusingyourcellphone-1106022...nekezh This document summarizes a business opportunity meeting for VMobile Technologies Inc. It outlines how becoming a VMobile dealer provides various ways to earn income, including through sales of access cards, endorsements of other dealers, and commissions from prepaid loads. It profiles three top earning VMobile dealers to exemplify the potential incomes attainable. The meeting promotes VMobile's services that offer discounts on prepaid loads through a centralized e-wallet system.
Advisor Recruiting



Advisor Recruitingjavidan This presentation is for financial advisors interested in making a change to the independent advisory side of the business.
Optify Best Practices - Lead Generation Campaigns



Optify Best Practices - Lead Generation CampaignsOptify In this presentation:
- Optify’s framework for lead generation campaigns
- Available lead generation channels
- Planning and setting up lead generation campaigns
- Executing lead generation campaigns
- Measure and report on campaigns
Understanding and Making the Most of Business Angels (Alan Barell) 



Understanding and Making the Most of Business Angels (Alan Barell) connectestonia The document discusses business angels and early stage financing. It provides an overview of different sources of financing including banks, venture capitalists, business angels, seed funds, and government grants. It describes the stages of investment from seed to expansion. The rest of the document focuses on engaging business angels, including how to impress them, find them, structure deals, and conduct due diligence. It emphasizes the importance of having a clear business model and plan to "show the money" to potential investors.
lennar 2000 annual



lennar 2000 annualfinance26 Lennar Corporation's 2000 annual report summarizes their strong financial and operational performance for the year. Key points include:
- Revenues grew 51% to $4.7 billion and net earnings grew 33% to $229 million, demonstrating strong growth.
- They completed a major acquisition of U.S. Home, diversifying their operations across the country.
- Returning value to shareholders through a 39% increase in shareholder's equity to $1.2 billion and a 33% growth in earnings per share.
- Lennar attributes their success to caring about their customers, associates, communities and managing for strong returns.
More from Venture Hacks (20)
AngelList Press Presentation, Oct 12 2015



AngelList Press Presentation, Oct 12 2015Venture Hacks AngelList is the world's largest marketplace for startup investing and jobs. It has raised $205 million online for startups in the last two years through syndicates, which are pop-up online venture funds. AngelList also facilitates over 52,000 job matching connections per month between candidates and startups. It announced a $400 million seed fund to invest in top syndicates and the launch of a new jobs app for iOS.
Anatomy of a (un)fundable startup



Anatomy of a (un)fundable startupVenture Hacks Naval Ravikant's talk at the 7th Founder Showcase. More at http://angel.co and http://venturehacks.com.
The rise of the angels



The rise of the angelsVenture Hacks The document discusses the rise of angel investors and how the venture capital industry is changing. It notes that startups are gaining leverage through cheaper access to capital from incubators, accelerators, and angel investors. Standardized documents and terms are becoming more common in angel investments. Predictions are made that more angel investors will enter the market, some startups may exploit investors, and some companies may skip venture capital funding altogether.
Venture Hacks for Kauffman Foundation



Venture Hacks for Kauffman FoundationVenture Hacks This document introduces the team behind Venture Hacks, including Babak Nivi and Naval Ravikant. It provides brief bios for each team member highlighting their experience in venture capital and startups. Short quotes are also included praising Venture Hacks from figures in venture capital and entrepreneurship.
VC signaling in seed rounds



VC signaling in seed roundsVenture Hacks Venture capital investors often signal valuable information to other investors through their investment decisions and level of participation in funding rounds. This signaling can influence whether other investors choose to participate. Seed investors typically make faster decisions with less paperwork than later stage investors. The level of participation from existing investors can signal whether a startup is worth further investment. Social proof from other investors is a rational factor in investment decisions.
How to close an angel round - Teaser



How to close an angel round - TeaserVenture Hacks 1. Use mass syndication to close an angel round by dropping names and not needing a lead investor.
2. Set terms and valuation below market, including price, liquidation preference, and majority control of amendments.
3. Describe how the terms are investor-friendly, such as no minimum raise and vesting as a pre-nuptial agreement.
How to close an angel round



How to close an angel roundVenture Hacks 1. To close an angel round, use "mass syndication" by dropping names of interested investors without a lead and writing your own term sheet with low valuations and investor-friendly terms.
2. Approach financing as if you won't find a lead and raise money before you need it with deadlines and social proof from interested investors.
3. Get introductions to seed stage investors through AngelList and StartupList and have traction in the form of a product in the marketplace before raising a seed round.
Presentation Hacks



Presentation HacksVenture Hacks This document provides tips and strategies for effective presentations and pitches. It emphasizes keeping presentations concise with a clear high-level concept pitch. The ideal elevator pitch summarizes the business on the back of a business card and follows the 10/20/30 rule of 10 slides, 20 minutes, and 30 point font. Traction, product, team, and social proof should be highlighted over lengthy descriptions. Preparation, storytelling, confidence and addressing investor interests are also important factors for a successful presentation.
How to optimize web apps with KISSmetrics



How to optimize web apps with KISSmetricsVenture Hacks The document discusses how to optimize web apps using KISSmetrics. It outlines that KISSmetrics helps optimize the user funnel by tracking user actions and metrics. It also allows calculating customer lifetime value. The document recommends using KISSmetrics for optimization after achieving product-market fit.
How to bring a product to market, Part 2



How to bring a product to market, Part 2Venture Hacks The document outlines Sean Ellis' advice for bringing a product to market. It discusses the importance of achieving product-market fit before focusing on growth. It recommends optimizing metrics, the customer funnel, and messaging when preparing for growth after achieving fit. It also advises growing quickly by using business models, channels, and nailing the initial user experience while leaving no room for competition.
How to measure product-market fit



How to measure product-market fitVenture Hacks The document outlines how to use the survey tool survey.io to measure product/market fit. It recommends asking customers questions about how they discovered the product, how they would feel without it, what alternative they would use, the primary benefit, if they have recommended it, what type of person could benefit most, how to improve it, and if follow up is okay. It also discusses getting qualitative feedback before fit is achieved and identifying must-have features by industry by asking the must-have question.
How to bring a product to market



How to bring a product to marketVenture Hacks The document outlines how to bring a product to market, with the first half focused on achieving product-market fit and the second half focused on preparing for growth after fit is achieved. It discusses how building a "must-have" product makes marketing easier, and provides tips for understanding customers, determining fit, communicating with investors, and pivoting based on customer feedback. The document recommends metrics for gauging fit and advises preparing systems and processes for scaling once the right product is validated.
Pitching Hacks Preview



Pitching Hacks PreviewVenture Hacks The document provides advice on obtaining introductions to investors by leveraging middlemen - people who investors respect and listen to. It emphasizes getting introductions from entrepreneurs and investors the target investor has backed, and avoiding introductions from investors who declined to back your company. The best way to get introductions is to craft a compelling high-level elevator pitch and deck that middlemen can forward with their recommendation.
How To Pick A Co Founder (Mini)



How To Pick A Co Founder (Mini)Venture Hacks The document outlines 16 topics for consideration when selecting a co-founder for a startup business, including how many co-founders are optimal, how to develop trust and shared history, how to divide ownership and responsibilities, leadership roles, necessary skills, and finding potential co-founders from personal or professional networks. It encourages aligning motivations and assessing a potential partner's skills in building and selling a product or service. The full interview on these topics is available for purchase.
Pitching Hacks at Stanford



Pitching Hacks at StanfordVenture Hacks This document provides tips for pitching startups to investors. It recommends focusing on telling a compelling story with traction through an introduction, high-concept pitch, and 10-slide deck rather than long-winded business plans or NDAs. Investors are more interested in the team, problem being solved, solution, and market fit than detailed plans or proprietary information.
The Lean Startup at Web 2.0 Expo



The Lean Startup at Web 2.0 ExpoVenture Hacks The document discusses the Lean Startup methodology. It contrasts two approaches to starting a company: a traditional plan versus a Lean Startup approach. The traditional plan focuses on raising capital, hiring experienced teams, building advanced technology, and promoting the vision. However, this often results in failure due to incorrect assumptions about customer needs. The Lean Startup approach emphasizes rapid iteration by building minimal viable products, getting customer feedback early, and continuously improving based on validated learning from real customers through metrics.
Vertical Markets



Vertical MarketsVenture Hacks The document discusses key considerations for high-tech startups. It outlines various vertical markets one could be in, such as web 2.0, enterprise software, or life sciences. It notes that startups must consider whether they face more market risk or invention risk. Finally, it lists numerous factors a startup must address during execution, including understanding the customer and competition, developing a business model and sales strategy, managing product development, and planning financial needs over time in order to successfully bring a new technology to market.
Customer Development 3: Introduction



Customer Development 3: IntroductionVenture Hacks This document discusses customer development as an important parallel process to product development for startups. It argues that startups often fail because they focus on product development without adequately engaging customers. The document introduces customer development as a process involving customer discovery, customer validation, and customer creation that should be synchronized with and guide product development. It emphasizes the importance of learning from customers over linear execution and achieving customer-centric milestones rather than focusing on the first customer ship date.
Customer Development 4: Customer Discovery Part 1



Customer Development 4: Customer Discovery Part 1Venture Hacks This document discusses customer development and outlines its key steps and methodology. It begins with an agenda that includes discussing the WebVan case study, testing problems and product concepts with customers, and establishing a customer development team. The rest of the document provides details on the customer development process, which involves testing hypotheses with customers through iterative phases of discovery and validation over several months or years. It emphasizes the importance of listening to customers, testing problems and products, and modifying the process for each individual company's needs.
Opening board meetings to the entire company



Opening board meetings to the entire companyVenture Hacks The document discusses opening up board meetings to all company employees and sharing both good and bad news more openly. It suggests running experiments under a different brand name to acquire customers on a small budget and test pricing in public. Employees providing critical feedback in board meetings could help everyone in the company better understand each other.
Recently uploaded (20)
Integrity e-commerce Trends FinTech 2025



Integrity e-commerce Trends FinTech 2025Ed Morrissey A brief presentation given during StL TechWeek's 2025 Fintech Summit on the lasting impact of the Covid pandemic on shopper behavior.
Laparoscopic UHD Imaging System Pitch Deck | March 2025



Laparoscopic UHD Imaging System Pitch Deck | March 2025Hector Del Castillo, CPM, CPMM Laparoscopic UHD Imaging System Pitch Deck
Kayretia "Lady K" Swatts Brand Identity Video



Kayretia "Lady K" Swatts Brand Identity Videoklswatts "Welcome to my personal brand video! This is where you get to know the person behind the work. I’m Kayretia "Lady K" Swatts a [Music Manager] In this video, I’ll share who I am, what I stand for, and the journey that led me to where I am today. Whether you’re looking for inspiration, collaboration, or just a deeper connection, I hope this video resonates with you. Let’s create something amazing together."
Advanced SystemCare Pro Crack Download 2025



Advanced SystemCare Pro Crack Download 2025bhutbhijan Direct Link Below🎁✔👇
https://upcommunity.net/dl/☝☝✅👉
Note: >> Please copy the link and paste it into Google New Tab now Download link And Enjoy 😍
Advanced SystemCare Pro is an all-in-one PC optimization utility designed for simplicity and efficiency
Raman Bhaumik - A Junior Software Developer



Raman Bhaumik - A Junior Software DeveloperRaman Bhaumik Raman Bhaumik is a Junior Software Developer passionate about technology and problem-solving. With expertise in Java, Python, JavaScript, and SQL, Raman has contributed to improving web application performance by 25%. Skilled in frameworks like React and Django, she is adept in API development, unit testing, and database optimization.
Hinduja Brothers - Pioneers of Global Business and Philanthropy



Hinduja Brothers - Pioneers of Global Business and Philanthropyshiveshmani09 The Hinduja Brothers are a prominent Indian-born British family who lead the Hinduja Group, a diversified global conglomerate. The four brothers are Gopichand, Prakash, Ashok, and the late Srichand Hinduja. Philanthropy is central to the Hinduja family's values. The Hinduja Foundation supports healthcare and education initiatives in India and the UK. Their philanthropic work includes building hospitals, supporting schools, and providing aid during crises. The Hinduja Brothers have built a legacy of business success and philanthropy, making significant contributions to both the global economy and society.
Selec Controls Company Profile FY25-26.pdf



Selec Controls Company Profile FY25-26.pdfSelec Controls Selec Controls Pvt Limited is one of India’s leading manufacturer in Electrical measurement, Electrical Protection & Control, power quality, solar, industrial automation, and process control, having a market reach in over 75 countries worldwide with three subsidiaries Selec GmbH, Selec Controls USA, and Selec Australia.
In India, with facilities spread over a 1.8 lakh sq. ft. area and over 4 million products manufactured per year, we are well known for our unique make-in-India vision, futuristic products, and exemplary quality that redefine excellence.
We have government recognized R&D center with NABL accredited lab enabling us to maintain the quality of the products to meet the industry standards.
Selec Control with a strong network of over 280 channel Partners worldwide, has supplied products to all types of industries and segments.
Selec has a workforce of more than 1000 employees in India and well-trained sales engineers across the country. To make the product selection to suit your technical and specified needs. We also have trained application engineers who can assist you with special application software for energy management solutions and industrial automation.
For on-site application support and after-sales services, we have a strong service network across the country.
Check out our website to know more: www.selec.com
Investment Opportunities in Semiconductor and Advanced Electronics Industries



Investment Opportunities in Semiconductor and Advanced Electronics IndustriesThailand Board of Investment North America Presented by Mr. Nanthapol Sudbanthad, Director of Thailand Board of Investment New York Office on April 2, 2025
Mohit Bansal_ The Green Visionary Behind GMI Infra’s Sustainable Legacy.pdf



Mohit Bansal_ The Green Visionary Behind GMI Infra’s Sustainable Legacy.pdfMohit Bansal GMI Discover how Mohit Bansal, CEO of GMI Infra, is redefining sustainable urban development with eco-friendly projects across Mohali. From green business hubs to energy-efficient homes, GMI Infra’s initiatives focus on reducing environmental impact while enhancing quality of life. Learn why GMI Infra is the go-to choice for sustainable real estate solutions.
Maharishi Vedic Approach: Exploring the Intersection of Vedic Philosophy and ...



Maharishi Vedic Approach: Exploring the Intersection of Vedic Philosophy and ...SerenePrana The Maharishi Vedic Approach to health is a holistic system rooted in ancient Vedic wisdom, combining philosophy, meditation, and Ayurveda to create a balanced and harmonious way of life. Maharishi Mahesh Yogi, the founder of the Transcendental Meditation (TM) movement, emphasized that true health is not merely the absence of disease but a dynamic state of balance between the body, mind, and environment.
The Most Influential Personality to Follow in 2025.pdf



The Most Influential Personality to Follow in 2025.pdfinsightssuccess2 This exclusive edition showcases Heena Ahuja the Director of HR at Relevance Lab & Cignex Technologies who carries over a decade of expertise in HR
T-shirt Printing Business New Business Idea



T-shirt Printing Business New Business IdeaSujeetPrajapati16 Department Of Commerce And Management Indira Gandhi National Tribal University Amarkantak Madhya Pradesh ( IGNTU) (New Business Idea) Course B.com/M.com & B.ba/M.ba Create And making By Sujeet Prajapati B.com 6th Semester And Final Year , Last Year
Bradley_Jamelia_BSEB_PB1_2025-03 Personal Brand Identity Kit



Bradley_Jamelia_BSEB_PB1_2025-03 Personal Brand Identity KitJABradley1 Bradley_Jamelia_BSEB_PB1_2025-03 Personal Brand Identity Kit
how to launch cosmetic d2c brand a complete roadmap



how to launch cosmetic d2c brand a complete roadmapSachinShukla868623 brand launch , customer insights , npd
The Role of Data Analytics in Shaping Leadership Trends_ARL_27 March 2025.pptx



The Role of Data Analytics in Shaping Leadership Trends_ARL_27 March 2025.pptxCharles Cotter, PhD The Role of Data Analytics in Shaping Leadership Trends by Dr Charles Cotter at the Africa Rising Leadership Summit and Awards on 27 March 2025. In this keynote presentation Dr Charles highlights three (3) research-based correlations between data analytics and leadership trends (2025 - 2030), namely:
• #1. The emergence and conceptualization of Evidence-based Management (EBM) thinking and -practices in transforming x4 organizational pillars into High Performing Organization (HIPO) sub-cultures
• #2. The power and value of harnessing data analytics in fuelling Data-driven Leadership best practices
• #3. The Future Fit Leadership Code - the four (4) most important currencies that future-fit business leaders trade in, in the context of the Collaborative Intelligence Economy (of the future).
Tran Quoc Bao: Asian Healthcare Leader and Top 10 Most Influential Hospital C...



Tran Quoc Bao: Asian Healthcare Leader and Top 10 Most Influential Hospital C...Ignite Capital Hospital Planning in Public-Private Partnerships: A Financial Framework for Success
By Dr. Tran Quoc Bao, Healthcare Industry Expert
In the rapidly evolving world of hospital Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs), understanding the underlying financial assumptions is crucial for successful project execution. Dr. Tran Quoc Bao, one of Vietnam's most influential healthcare leaders, emphasizes the importance of a detailed financial model when planning hospital infrastructure through PPPs. This approach helps sponsors, particularly in greenfield projects, estimate capital and operational needs with greater precision.
A key component of this model is the breakdown of construction costs, which are typically estimated at $2,000 per square meter. The model suggests varying space requirements per bed depending on the region: 120m² in Emerging Markets, 170m² in Western Europe, and a significantly larger 360m² in the U.S. These differences reflect regional healthcare standards, and understanding these variations is critical for accurate cost forecasting.
Ongoing capital expenditures (capex) are also a significant consideration. This includes 2.5% for building maintenance and 15% for equipment costs, ensuring that the financial model aligns with real-world expectations. Operating costs per bed typically range from $120,000 to $160,000 annually. This financial framework also includes assumptions about debt-equity ratios (70/30) and a base loan interest rate of 12%, offering insight into project financing.
A vital component of the model is the expected return on equity (ROE), which ranges between 16-18%. This figure provides valuable guidance for investors in understanding the long-term financial sustainability of hospital PPP projects. Moreover, Dr. Bao highlights that upfront capital expenditure subsidies can substantially reduce annual PPP payments, providing governments and sponsors with greater flexibility in structuring agreements.
This comprehensive financial framework offers crucial clarity for hospital PPPs, allowing investors and sponsors to make smarter, more informed decisions about healthcare infrastructure development. By embracing these financial principles, stakeholders can enhance the predictability of costs, optimize resource allocation, and ultimately ensure the success of hospital PPP projects across various markets.
Value Chain Framework Powerpoint Template and Guide



Value Chain Framework Powerpoint Template and GuideAurelien Domont, MBA The Value Chain tool is useful to design a map of all the activities within a Business or an industry. It helps to disaggregate a business/industry into its ‘value’ activities. It can be used to compare industries and firms or to determine and analyze costs.
This PowerPoint presentation includes a Value Chain Framework template and guide. It is only a small preview of our content. For more details, visit www.domontconsulting.com
Investment Opportunities in Semiconductor and Advanced Electronics Industries



Investment Opportunities in Semiconductor and Advanced Electronics IndustriesThailand Board of Investment North America



